In Your Face: The Future of Federated Patient Identification

The following guest post was written by Michael Trader, Co-Founder and President of RightPatient®
The Patient ID Problem
The recurring and complex issue of how to establish and maintain accurate patient identification in healthcare and how to establish a federated patient identity is getting a lot of attention these days. Accurate patient identification in healthcare is a topic that has always garnered attention and concern, but perhaps it has gained momentum and urgency due to the rapid digitization of the industry and the concerted push for interoperability and national health information exchange to improve individual and population health. The push for increased interoperability could make patient data matching errors and mismatches exponentially more problematic and dangerous and it is widely believed that inadequate patient identification continues to jeopardize patient safety and artificially inflate the cost of care.

Can the use of facial recognition biometrics help establish a federated patient identity credential in healthcare?
Opinions on the most effective patient identification and patient matching strategies run the gamut. Some say standardizing patient demographic data will help, others feel that establishing a national patient identifier is the answer to the problem. What’s clear is that in the absence of any broad improvements to patient identification, the goal of establishing longitudinal patient records reflecting a patient’s experience across the care continuum, payers, geographic locations, and stages of life, will remain elusive.
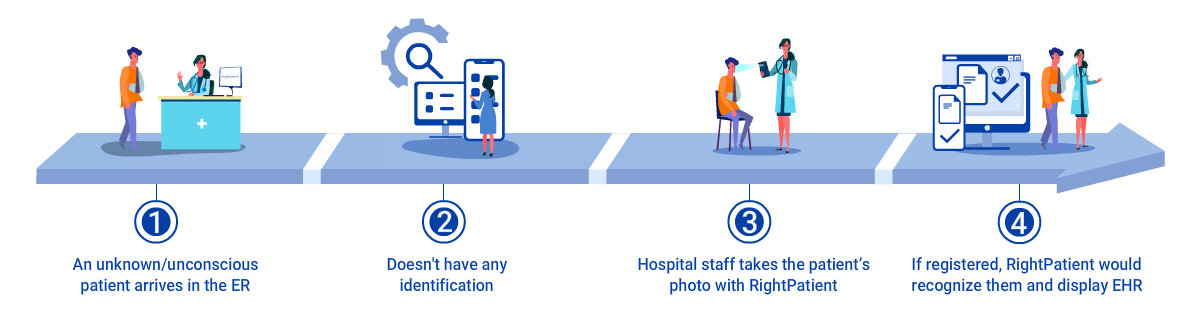
One idea that is catching on with healthcare providers to help improve patient identification in healthcare is capturing a photo during registration that is linked to a unique electronic medical record.
Use of Patient Photos Increasing
Nearly 2.3 million people were victims of medical identity theft in 2014, according to the “Fifth Annual Study on Medical Identity Theft” released earlier this year by the Medical Identity Fraud Alliance (MIFA), an industry trade association of healthcare providers, payers and service providers – a 21% increase over the 2013 number of 1.8 million. Medical identity theft and healthcare fraud continue to be a pervasive problem throughout the industry and in the absence of a solution, the problem is only going to get worse as millions more Americans are brought into the healthcare fold through Obamacare.
To help fight the increase in medical identity theft and to ensure a patient’s identity is accurately verified at each step along the care continuum, many healthcare facilities are capturing a patient’s photo at registration and linking that to a unique electronic medical record. The idea is an attempt to protect patient privacy, ensure accurate insurance benefits and subsequent reimbursement, and connect a face with a name, providing another option for identification besides date of birth. The idea is catching on quickly and many are embracing the use of patient photos to increase security and improve patient safety, but what often goes unrealized is the potential for a patient photo to be leveraged as a unique identification credential across the entire care continuum.
Leveraging Patient Photos for a Federated Identity Across the Care Continuum
Whenever we hear the words “patient identification” most of us envision sitting across a registration desk at a hospital or doctor’s office providing demographic data and our driver’s license and/or insurance card. However, patient identification in healthcare has evolved to now include accurate identification at each and every patient touchpoint along the care continuum including patient portals, mhealth apps, telehealth, and home health just to name a few. One of the smartest strategies to ensure accurate patient identification at any point along the care continuum is to capture a patient’s photo at registration and then leverage that photo along the care continuum through biometric facial recognition technology.
Let’s take patient portals for example. Most of us know that Meaningful Use Stage 2 mandates that healthcare providers provide patients the ability to electronically view, download, and transmit health information. The most popular means to that end is the increasing use of patient portals yet many providers rely on antiquated identification protocols such as user names and passwords to protect access to this personal health information (PHI). The problem is relying on user names, passwords, and/or personal identification numbers (PINs) is risky and could potentially open the door to third party data breaches which are decimating the industry and exposing millions of patients’ PHI.
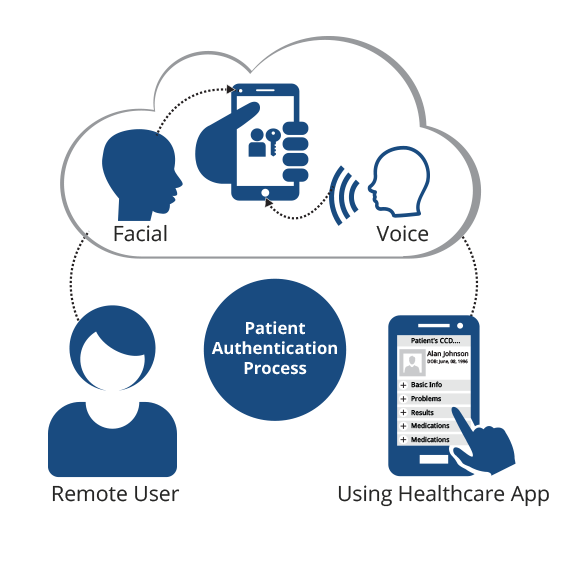
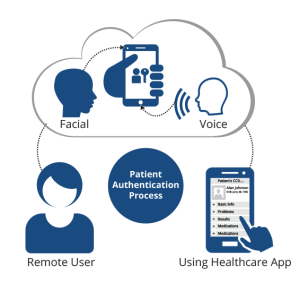
As an alternative to using user names and passwords, consider a healthcare organization that captures a patient’s photo during registration. Not only is that photo visible to patient registration staff and clinicians at each episode along the care continuum as a second form of multi-factor authentication, but if a patient signs into a patient portal and the hospital has deployed facial recognition identification to authorize a patient’s identity prior to logging in, the hospital has just successfully leveraged that photo as an identification credential for access to their PHI. Same goes for mHealth apps. Biometric patient identification providers that offer the value and flexibility of facial recognition authentication can also help third party developers and healthcare providers add this technology to off-the-shelf (OTS) or custom mHealth apps as a more secure way of identifying patients with the ability to work with any standard camera.
Coupled with the fact that 80% of patients are open to healthcare interactions on smart devices but remain highly sensitive to sharing health data, facial recognition biometrics for accurate identification has already proven itself as a more secure alternative than user names and passwords not to mention the fact that 69% of 16 -24 year olds recently polled indicated they believe biometrics will be faster and easier than passwords and PINs and half foresee the death of passwords by the year 2020.
Writing on the Wall?
With predictions that 50% of smartphones sold by 2019 will have a fingerprint sensor and over a billion biometric mobile devices will ship worldwide by the year 2020 (all equipped with cameras sophisticated enough to use facial recognition), the evolution of patient identification in healthcare is tilting more towards the use of biometrics to replace user names, passwords, and PINs as the preferred method of authentication due to it’s increased security and the flexibility to apply the technology for accurate identification at more patient touchpoints borne from the rapid digitization of the industry. Considering the fact that 41% of consumers stress over smartphone mobile security and biometrics are already overtaking passwords as the de facto identification credential on smartphones, could this be the perfect storm for a rise in the use of facial recognition for accurate patient identification?
Responsible approaches to improving patient identification in healthcare must now include addressing accuracy at any touchpoint where a patient can now access PHI. The advent of facial recognition as a unique identifier in a singular or multi-factor environment is a smart answer to the challenge of ensuring a patient receives accurate care throughout the continuum no matter if they are physically present or accessing services from cyberspace.
Since more patients expect providers to ensure privacy and protect their PHI, is it time to more closely examine implementation of a patient identification solution that leverages biometric facial recognition?
 Michael Trader is President and Co-Founder of RightPatient®. Michael is responsible for overseeing business development and marketing activities, government outreach, and for providing senior leadership on business and policy issues.
Michael Trader is President and Co-Founder of RightPatient®. Michael is responsible for overseeing business development and marketing activities, government outreach, and for providing senior leadership on business and policy issues.