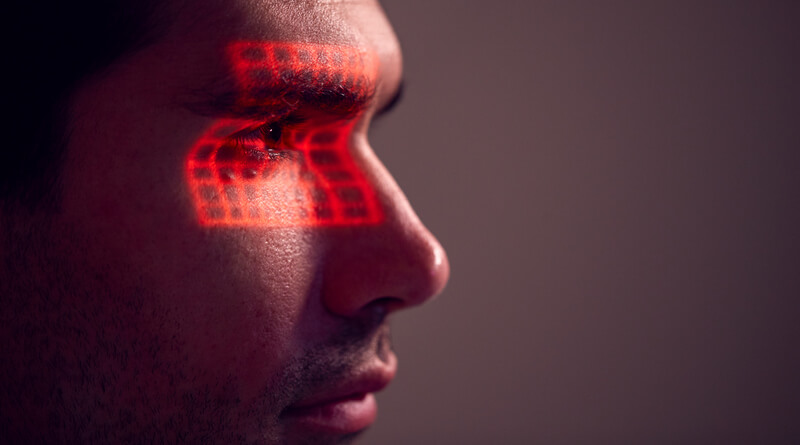
Enhance Patient Safety – Are you using a touchless solution for patient identification?

We are living through the COVID-19 pandemic. In times of crisis, the ability to provide treatments quickly and delivering clear communication are crucial. The U.S healthcare system is responding to this crisis by detecting, testing, treating, isolating, and mobilizing patients as well as healthcare staff members. However, how healthcare providers are identifying their patients remains a key concern. Are they using contact-dependent or touchless solutions? Touchless solutions for patient identification have many benefits over contact-dependent options. Especially during a pandemic, the most important one might be obvious – they are ideal for hygiene and infection control. This can play an important role in patient safety.

The COVID-19 outbreak has been a prime catalyst for the growth and adoption of touchless identification processes. Many healthcare providers are also looking for ways to enhance patient safety while they secure a patient’s identity and their medical records in a hygienic manner. Let’s examine both contact-dependent and touchless solutions for patient identification with regards to hygiene and infection control.
Infection control concerns about fingerprint and vein scanners
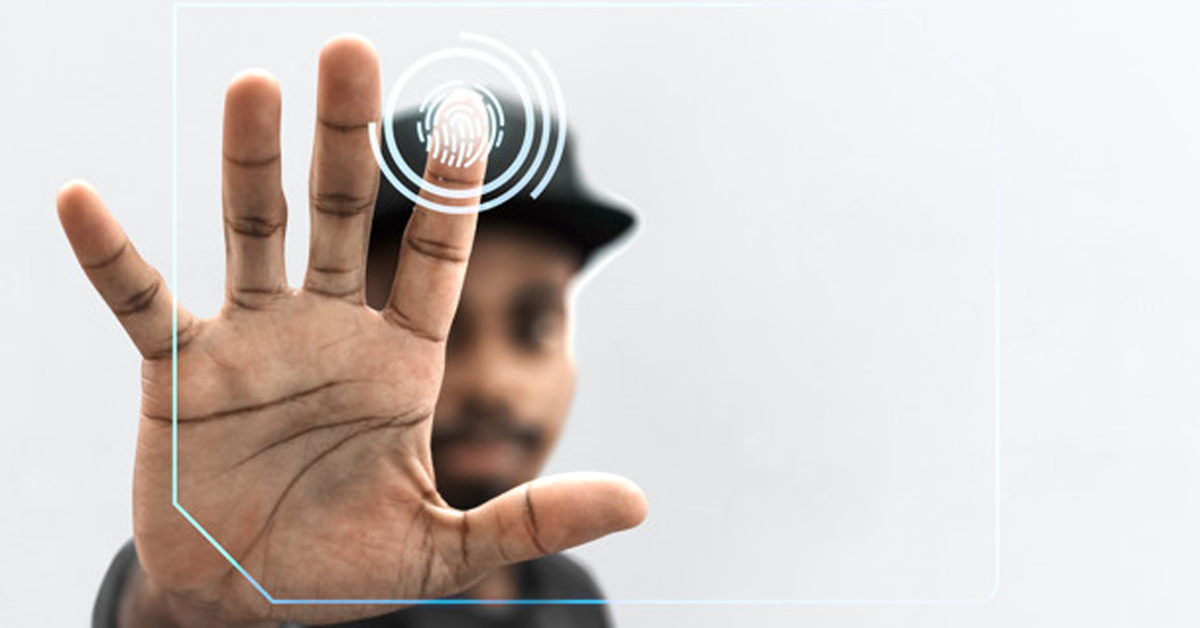
Fingerprint and vein recognition models for patient identification are currently used across the U.S. healthcare system. However, hygiene and infection control must be considered with these contact-dependent biometric scanners. Since the COVID-19 outbreak, numerous studies have determined that there is a risk of infection through commonly touched surfaces. Reports determined that this virus can survive from hours to days depending on the type of surface the particles land on. For fingerprint recognition, patients are required to touch a sensor that carries a level of surface contamination that is equivalent to door handles.
Vein recognition, on the other hand, requires users to place their entire hand or finger on a plastic mold that helps with proper positioning over the biometric sensor. This increases the amount of contact-dependent surface area and overall risk.
In addition, fingerprint and vein scanner surfaces need to be cleaned after each use to prevent the risk of infection transmission. This necessary precaution introduces an additional cost and resources burden for healthcare providers while preventing employees from focusing on more important tasks.
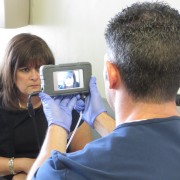
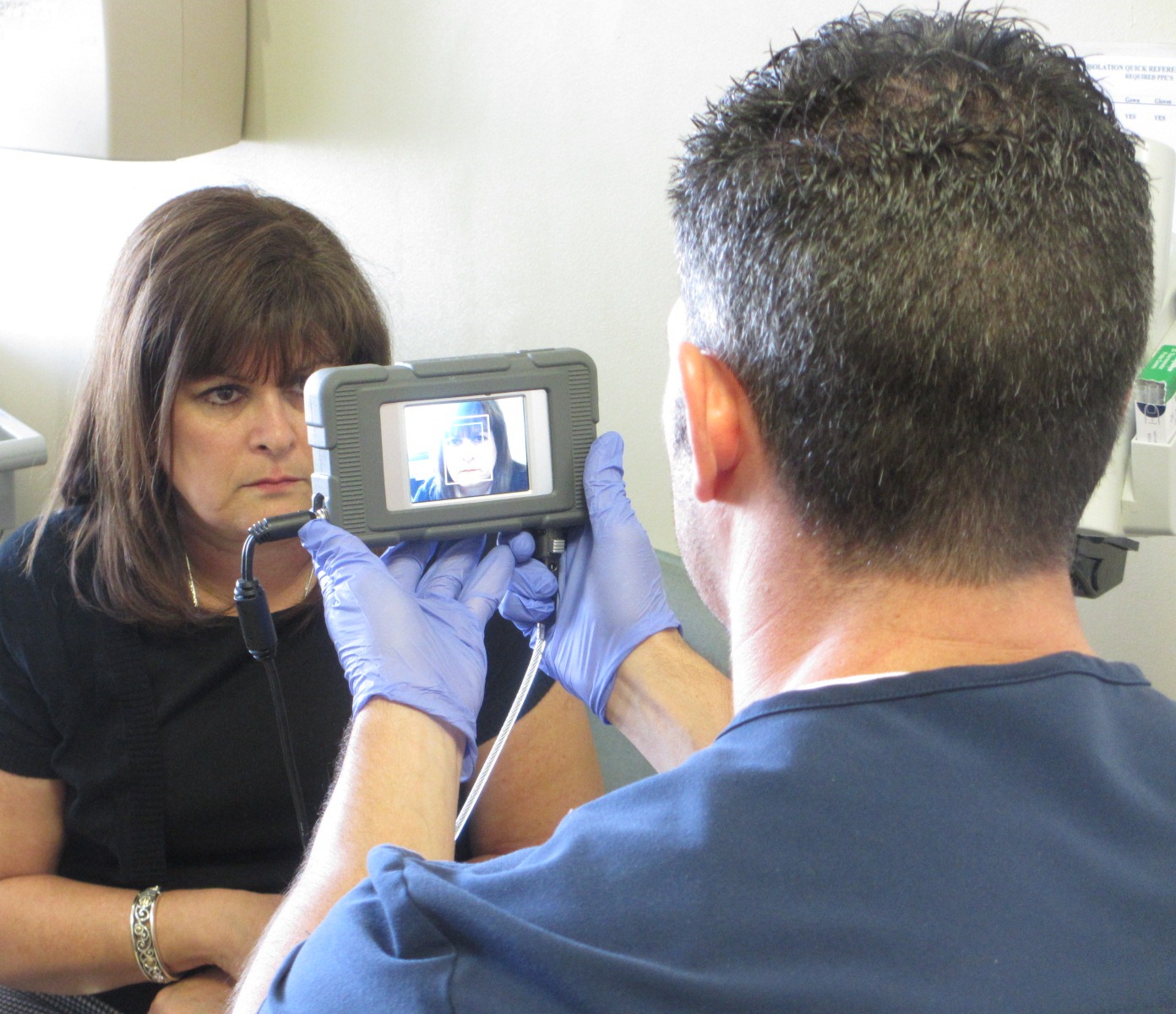
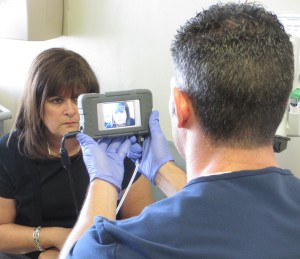
Facial and iris recognition modalities for patient identification
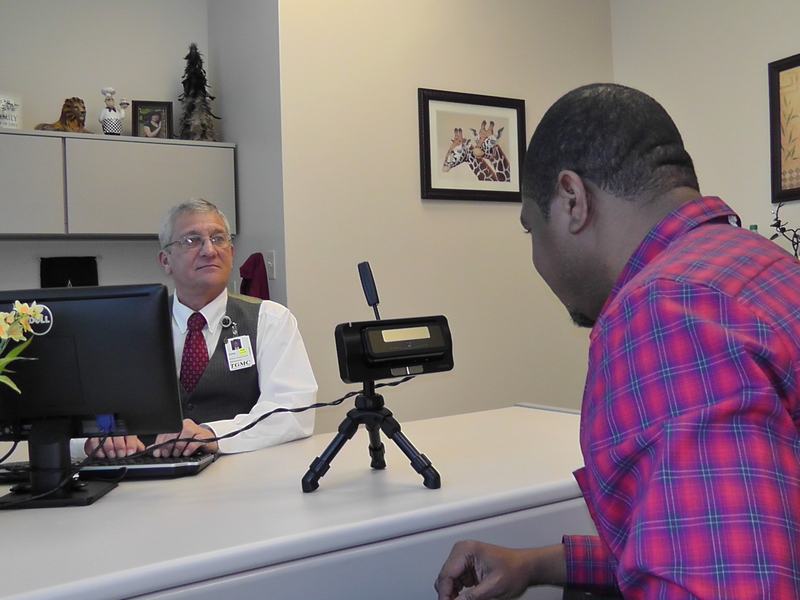
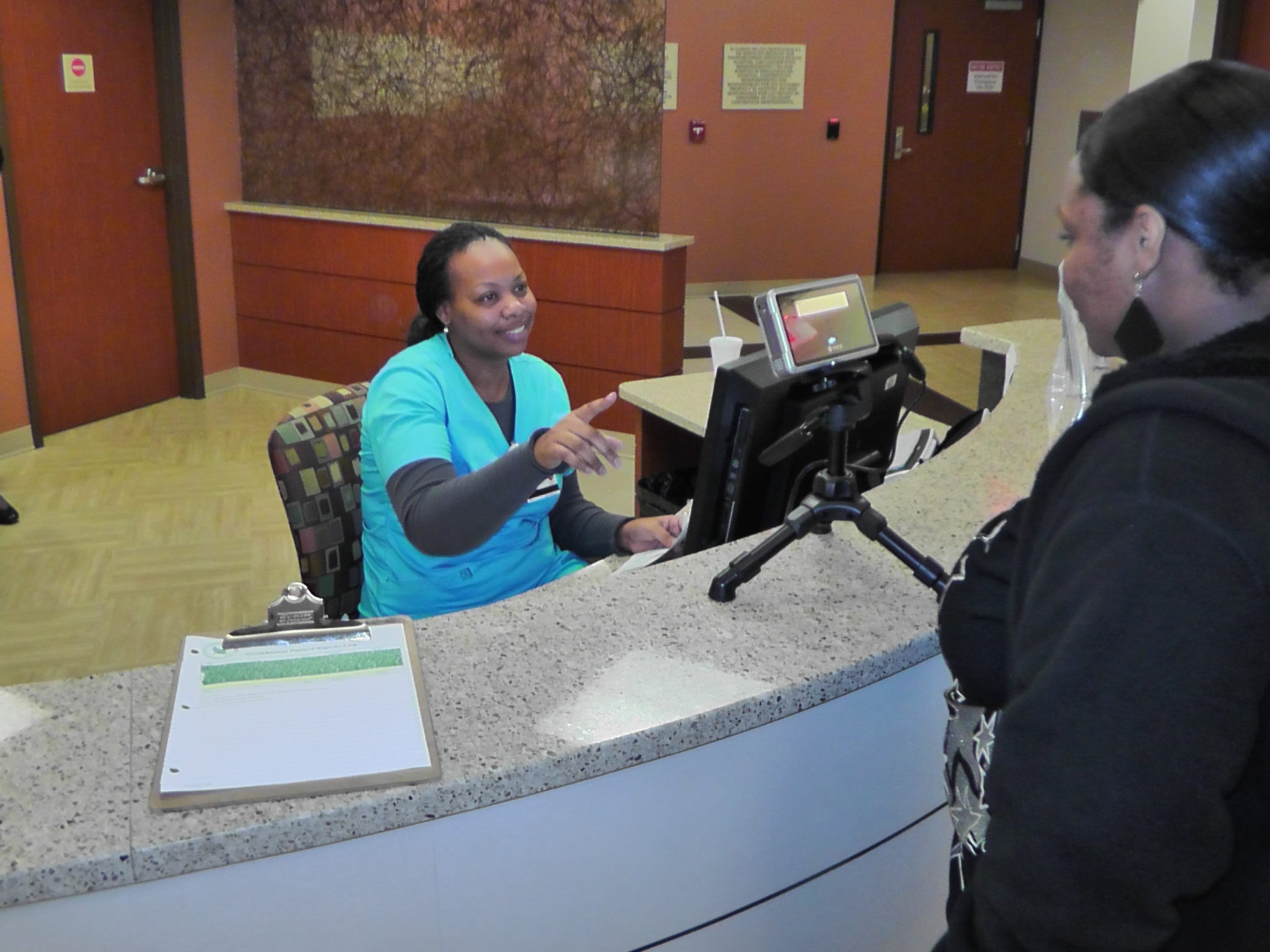
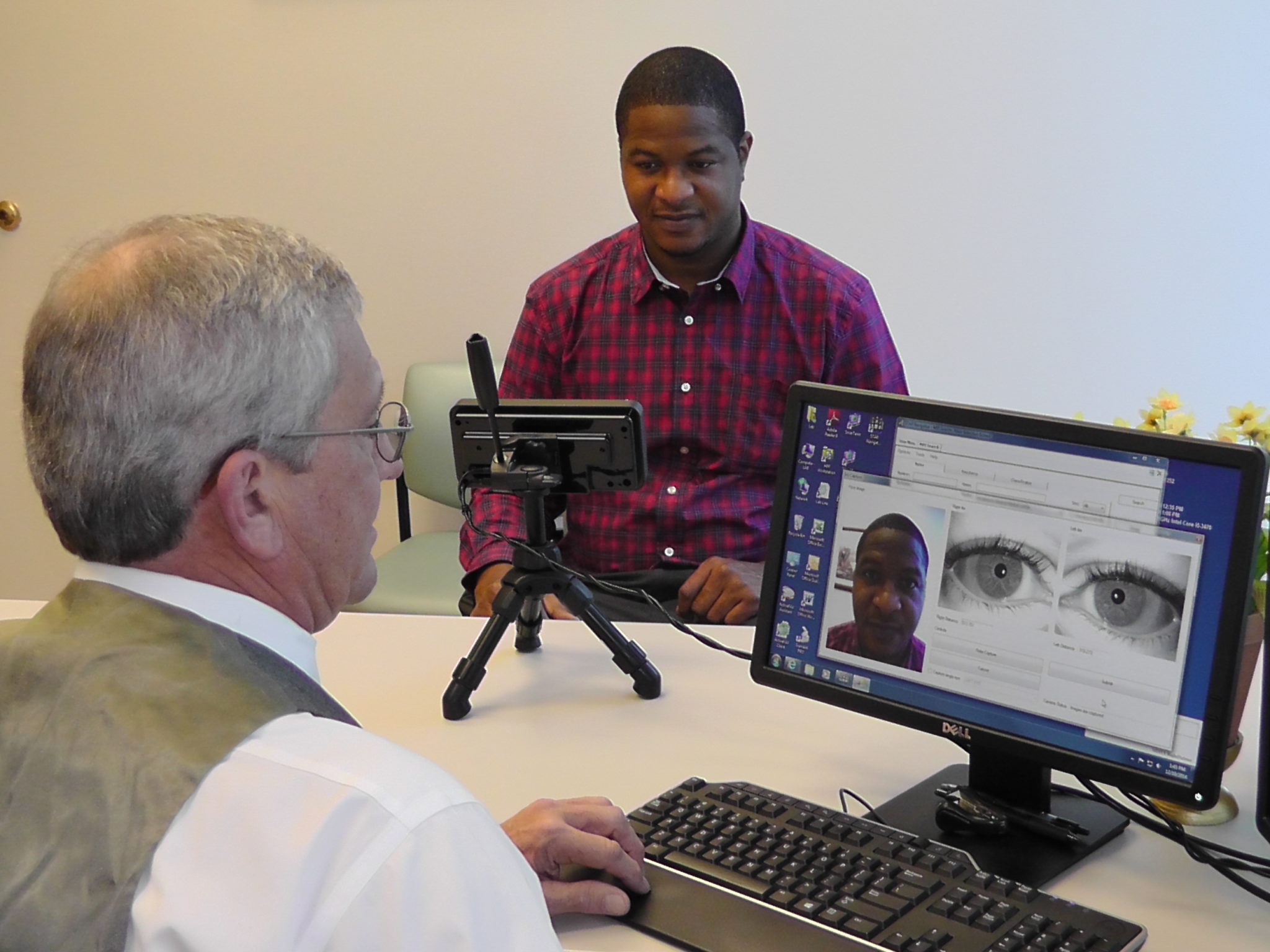
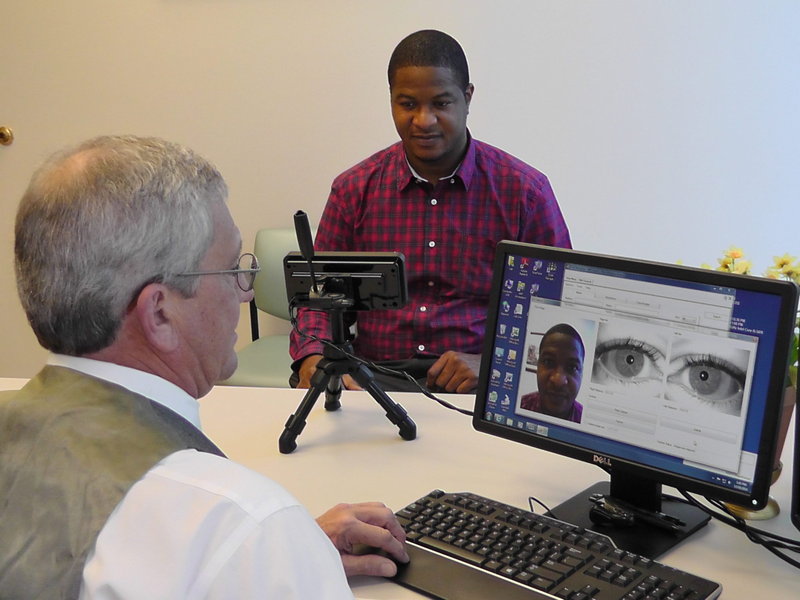
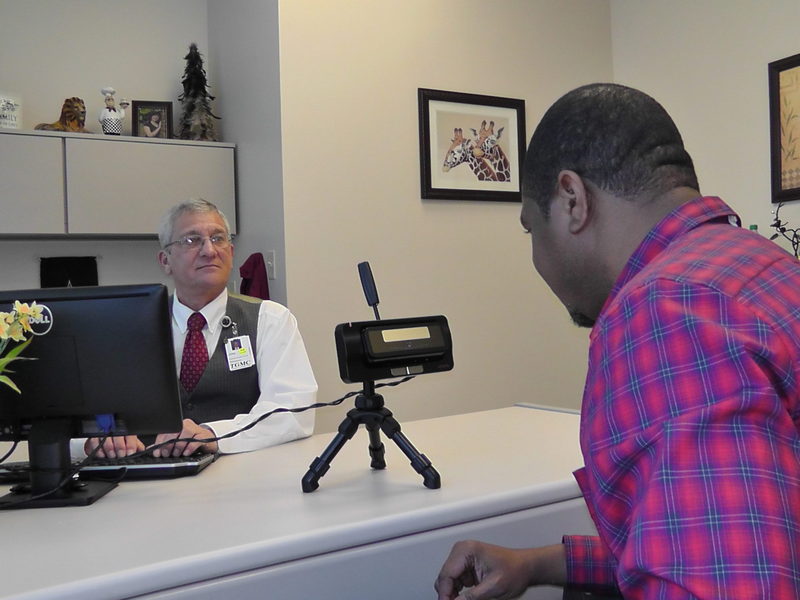
Touchless patient identification systems such as facial or iris recognition, on the other hand, completely eliminate the risk of spreading infection by allowing patients to be identified without needing to touch anything. Furthermore, according to a study, iris recognition has a far better success rate for identification compared to fingerprint recognition.

Besides being more accurate, iris and facial recognition techniques will enable healthcare providers to identify their patients from a safe distance. By eliminating patient identification errors, hospitals can enhance patient safety while ensuring a hygienic environment, without even needing to constantly sanitize scanning devices or sensors.
Enhance patient safety with RightPatient
Several studies suggest that touchless biometric identification is about to experience significant growth. Now that the difference between contact-dependent and touchless solutions is clear, choosing the right vendor will play an important role. Several leading hospitals have already experienced an improved revenue cycle by eliminating duplicate medical records and medical identity theft since using RightPatient – the leading touchless biometric patient identification platform. Some customers include Community Medical Centers, University Health Care System, and Terrebonne General Medical Center.
Aspects of our lives that we have been taking for granted have been threatened by the COVID-19 outbreak. Our fears and concerns about spreading the virus have been elevated, and healthcare providers are taking any and all necessary steps to protect their patients and their staff members. Clearly understanding the risk factors associated with contact-dependent biometric patient identification devices and considering RightPatient’s touchless patient identification platform can be an effective way to reduce risk and enhance patient safety.