The following guest post was written by Brian Bilia, Enterprise Sales Consultant with RightPatient®
More Schools Using Non-Contact Biometrics for Individual Identification
In case you missed it, this week Virginia Commonwealth University announced the implementation of iris recognition in their on-campus dining halls for student identification. In addition to presenting a safer and more secure way to identify students the deployment according to the article, the initiative is designed to be:
“…helpful for students who forget or lose their IDs over the weekend, as there is not a way to get a replacement card over the weekend.” (USA Today, “New iris cameras at Va. school scan students’ eyes for entry into dining hall” http://usat.ly/1L4cbWb)
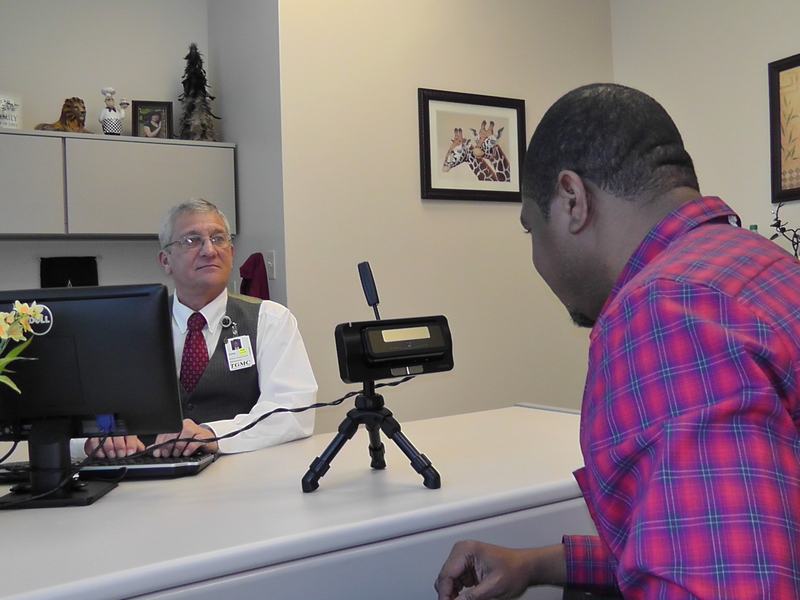

If schools adopt iris biometrics for student ID based on it’s non-contact, hygienic form factor, shouldn’t the healthcare industry offer the same protection to patients?
The article goes on to report that one of the main reasons Virginia Commonwealth and another schools chose to deploy iris recognition was because of its non-contact, hygienic feature:
“VCU is following in the steps of other schools — including George Mason University — which introduced the eye scanning system last year. Both schools opted for the this non-contact form of biometric technology — as opposed to a fingerprint scanner — because it is less invasive and won’t spread germs.” (USA Today, “New iris cameras at Va. school scan students’ eyes for entry into dining hall” http://usat.ly/1L4cbWb)
Essentially, hygiene played a critical role in determining which biometric modality the school would use for student identification. Due to the fact that iris recognition does not require physical contact with a biometric device, it presents one of the most hygienic hardware options available, keeping end users safe from the spread of germs and illness that could otherwise be a risk when using a contact dependent modality such as fingerprint or palm vein recognition. The fact that schools continue to adopt iris recognition for identification due to it’s hygienic, non-contact features begs the question — shouldn’t hospitals adopting biometric patient identification tools be investigating non-contact biometric modalities too?
Non-Contact, Hygienic Biometric Patient ID in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, patient safety is the #1 priority. Rising conscientiousness about new strategies to keep patients safe rise combined with the explosion of digital health tools has pushed hospitals to re-assess hospital acquired condition (HAC) control policies and implement new platforms and monitoring programs that provide a safer and more hygienic environment for patient care. In addition, new policies by Medicare now penalize hospitals with high HAC rates raising the level of urgency to adopt digital health tools that support hospital infection control policies.
In lockstep with the urgency to increase patient safety in any possible way, hospitals and healthcare organizations are quickly catching on to the benefits of using biometrics for patient identification as a means to increase patient safety but what they are also discovering is that not all biometric hardware modalities have the ability to offer a non-contact, hygienic experience. Biometric hardware that requires physical contact by a patient can be interpreted as non-hygienic and raises the risk of HAC’s if the device is not properly sanitized after each use. Even when properly sanitized, these devices still pose a threat to patient safety due to the fact that cleaning agents do not have the ability to remove 100% of germs or bacteria.
Upon further research, healthcare entities learn that using iris recognition for patient identification in healthcare offers the use of an iris camera that a patient does not touch, helping to support hospital infection control policies and ensure that no one is susceptible to germs or bacteria that could cause an infection or illness.
Patient Acceptance is Key
Despite the advantages of using iris recognition for patient ID in healthcare, certain stigmas exist about this technology that may make a healthcare organization hesitant to adopt. Many feel that iris recognition is too invasive and beams visible light into a patient’s eyes to determine their identity. In reality, iris recognition is often confused with retinal scanning which does use visible light for identification. Iris recognition instead uses camera technology with subtle infrared illumination to acquire images of the detail-rich, intricate structures of the iris. It’s 100% safe, and our field research has proven that patients are overwhelmingly accepting of using iris recognition for identification when presented with the option to protect them from duplicate medical records, fraud, and medical ID theft.
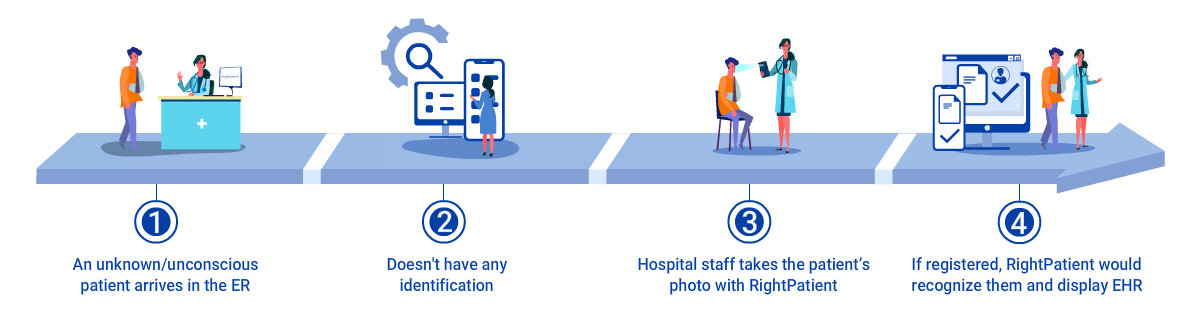
Plus, iris recognition for patient ID offers other benefits such as the ability to identify unconscious or unknown patients and is built on one-to-many matching, the only true way to prevent duplicate medical records and medical identity theft in healthcare.
Conclusion
Iris recognition has proven to be one of the most popular biometric modalities for individual identification for a number of reasons, including it’s non-contact, hygienic form factor that protects end users from germs and bacteria that otherwise exist on alternative biometric hardware devices. Hygiene has a rising influence in determining which hardware modality is utilized in biometric identification management projects, and the advantages of using iris recognition biometrics has positioned the technology for strong adoption growth in the years to come.
How important is hygiene to you when selecting a biometric hardware modality?

Brian joined RightPatient in July 2015 as Enterprise Sales Consultant for the Midwest Region. Prior to RightPatient, Brian held several roles in sales management and new business development achieving over 15 years of experience working with the healthcare/hospital industry.