How Wearables Improve Patient Identification and Reduce Medical Errors
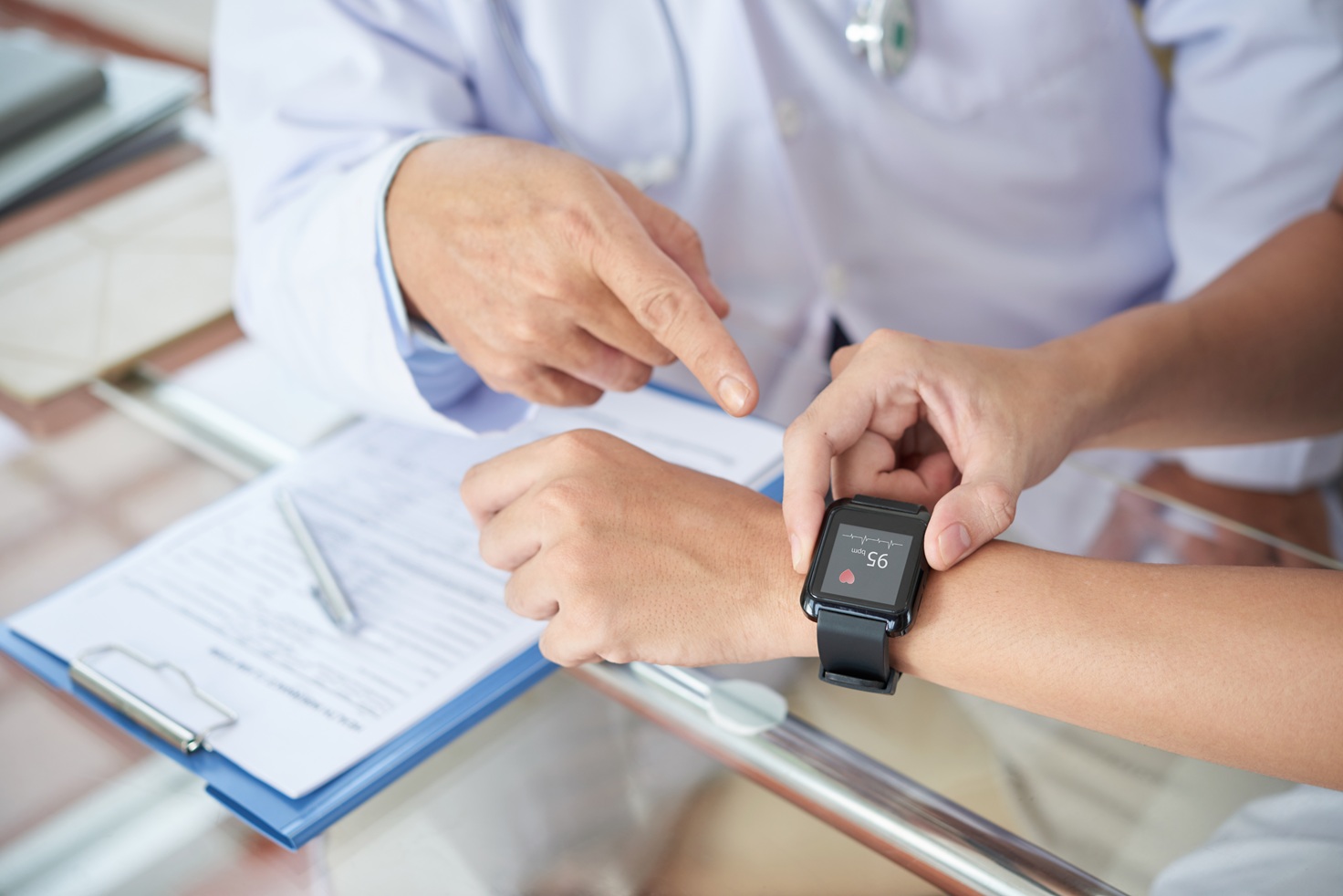

Even in big hospitals and clinics, the slightest identification error can result in severe medical errors, and patients deserve safer, more reliable identification.
That is why wearable technologies are gaining such significance in today’s healthcare. Imagine wristbands that will automatically connect to electronic health records, or smart sensors that verify a patient’s identity even before any treatment is given.
These technologies aren’t just impressive gadgets; they do the work of reducing risks, assisting both nurses and doctors, and making the overall care delivery process safer and easier for patients and all stakeholders involved.
This article will discuss both the use of wearables to identify patients and the reasons why they are increasingly becoming an important tool in the fight against preventable medical errors.
The Patient Identification Problem in Healthcare
If you’ve ever watched nurses double-check a patient’s wristband, you’ve seen just how seriously healthcare teams treat identification. And they have good reasons. Even confusing two patients with similar names can result in delayed treatment, wrong medication, or even an incorrect diagnosis.
A review of reported “sentinel events” in the U.S. between 2014–2017 found that 409 out of 3,326 events (≈ 12.3%) were associated with patient‑identification errors.
Such errors are not necessarily due to negligence but are often caused by increased hospital workload, the many tasks an employee must handle, and the fact that manual checks are not foolproof.
The conventional approaches, such as paper wristbands or confirmation by word of mouth, are useful, but they are largely dependent on the human factor. When emergencies occur, shifts change, or there is a language barrier, the chances of being mistaken will rise relatively fast. This is why a lot of medical workers are seeking more stable, technology-oriented solutions.
What Wearable Devices Bring to Patient Identification
Wearables are changing how patients are identified in hospitals. Smart wristbands or ID patches can link patients directly to their medical records, eliminating the need for manual checks or guesswork.
These machines minimize errors such as prescribing the wrong medicine or delaying treatment, which gives patients and medical workers greater confidence. In addition to safety, wearables save time, enabling nurses to concentrate on care, as opposed to paperwork.
Simply put, they are small devices with a big effect by enabling the identification of patients quickly, more precisely, and, overall, less stressful to all parties involved.
Wearable-Led Patient Identification Use Cases
Emergency Rooms: In high-traffic emergency rooms, time is of the essence. Smart wristbands provide the medical staff with immediate access to the medical history, allergies, and current medications of a patient. This real-time availability of information enables quicker, more informed decisions in life-threatening situations.
Surgical Units: Before a patient goes under the scalpel, it is important to check their identity. Wearable devices and ID patches ensure the correct patient is associated with the correct procedure, minimize the risk of surgical errors, and increase overall patient safety.
Pediatrics and Geriatrics: Children and the aged are also vulnerable groups that are most likely to suffer from misidentification. With wearables, there are no mistakes made when similar patients or patients with similar conditions are mixed.
Real-Time Alerts: Wearable devices are able to provide real-time alerts on important health occurrences (like an abnormal heart rate or a medication reminder), which are connected directly to medical records and can be acted upon by staff.
General Productivity: These miniature devices, in addition to safety, make the functioning of hospitals more efficient, enhance the accuracy of the records, and allow personnel to devote more of their time to patient care, but not to administrative matters. Wearables will make the healthcare setting smarter, safer, and more efficient when they are combined with technology and patient-centered practices.
Integrating Wearables Into Clinical Workflows
Integration of wearable patient ID devices should be carefully planned, and workflow changes should be properly addressed to be successful. The hospitals should educate personnel on the timing and methods of scanning or syncing devices in the admission process up to the moment of discharge to ensure that data is recorded at each stage in an accurate manner.
EHR systems should be able to be updated by wearables in real-time and provide clinicians and nurses with the necessary information about a patient at any time. The hygiene, maintenance, and consent of a patient of the device should also be identified in clear policies that will assist in safeguarding both safety and privacy.
Upon integration, wearables can be used to cut down paperwork, save the time of staff members, and simplify day-to-day operations. Identification errors are reduced to the level of minimal or even nonexistent, communication between care teams is quickened, and the medical professionals are able to concentrate on what really counts: timely and high-quality care of the patients.
AI’s Role in Enhancing Wearable-Based Patient Identification
Wearables are becoming smarter with the help of AI in identifying patients and identifying them accurately and quickly. By analyzing vitals, medical histories, and even genetic data, AI can compare patients with the appropriate records, preventing errors even before they occur.
Together with intelligent wristbands or ID patches, such systems will notify the clinicians in real time in case of a possible mismatch, which will make hospitals safer and care more effective.
As UpMarket notes, AI-powered wearables are not mere technological devices; they can actively assist healthcare teams, reduce identification errors, and help patients receive the appropriate treatment at the right time.
Cost of Wearable Patient ID Solutions
Investment in wearable patient identification systems may seem like a heavy burden, yet the gains usually outperform the expenditures.
Based on ScienceSoft’s experience in building EHR-based remote patient monitoring systems, full project costs typically range from $200K to $400K, depending on required functionality and regulatory demands. These solutions usually include real-time data synchronization, AI/ML analytics, and clinical decision support.
Although this can seem substantial in the short term, such solutions will be able to radically lower the number of medical errors, improve workflow optimization, and enhance patient safety. Wearable-based identification is not only a technological enhancement in the long term, but it is also a wise investment in efficiency, precision, and tranquility within healthcare staff.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Security and privacy are not luxuries when it comes to wearable patient ID solutions; they are essential. These gadgets store vital medical information, including heart rates and medication times, and any hacking may be fatal. This is why encryption, secure data storage, and strong access controls are considered priorities for hospitals and developers.
The patients will be more relaxed knowing that their data is secured yet readily accessible as and when necessary by the healthcare providers. Privacy laws, such as HIPAA in the U.S., establish straightforward guidelines on how patient information ought to be processed, and wearables that comply with these guidelines simplify adherence.
In addition to being regulatory compliant, it is important to develop trust with the patient, honesty in explaining what types of data are being gathered, the usage of the data, and who may see it, is important in developing confidence. In brief, a smart wearable is excellent, yet a secure one that does not violate privacy? That’s truly next-level care.
Benefits for Providers and Patients
For providers, such devices simplify processes, minimize administrative errors, and ensure the right treatment is given to the right patient at the right time. This will translate to reduced stress, errors, and more time to concentrate on the actual patient care.
Patients are provided with more security and peace of mind. The chances of the wrong medication or treatment are reduced because there is instant access to the correct medical records. Vital signs can be monitored through wearables in real time, which provides the provider with a quicker response to changes of any concern.
These devices eventually make the healthcare experience more efficient and smooth. Incidents of providers working harder, patients feeling safe, and the quality of care become better. Wearables are smart, simple, and practical, and hence, a win-win for all.
Challenges and Best Practices for Adoption
Implementing patient ID solutions that require wear is not without its problems. The hospitals can be expensive, face integration challenges with current EHR systems, and have employees who might be reluctant to adopt new technology. Patients can also be concerned with the privacy of health data or be inconvenienced by the surgery of wearing gadgets.
Nonetheless, adoption can be made easier by best practices. Begin with the obvious training of staff to make them confident and use them correctly. Considerably add devices to current processes rather than replacing systems during one night.
The most important thing is communication – it is possible to make people accept it by explaining the benefits, concerns, and mentioning improvements in safety and efficiency. Wearable patient IDs can improve care and prevent errors, resulting in a safer, smoother healthcare experience when applied intelligently.
Conclusion
Wearable patient identification solutions are transforming the healthcare sector by rendering patient identification secure and more dependable. Medical staff can instantly access correct information and save time by using smart wristbands and devices operated with the help of AI.
These tools contribute to efficient workflow and care in hospitals by securing patient privacy and enabling hospitals to work efficiently and concentrate on care. Wearables are small, practical, and efficient, and enhance the experience of patients and healthcare teams.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!