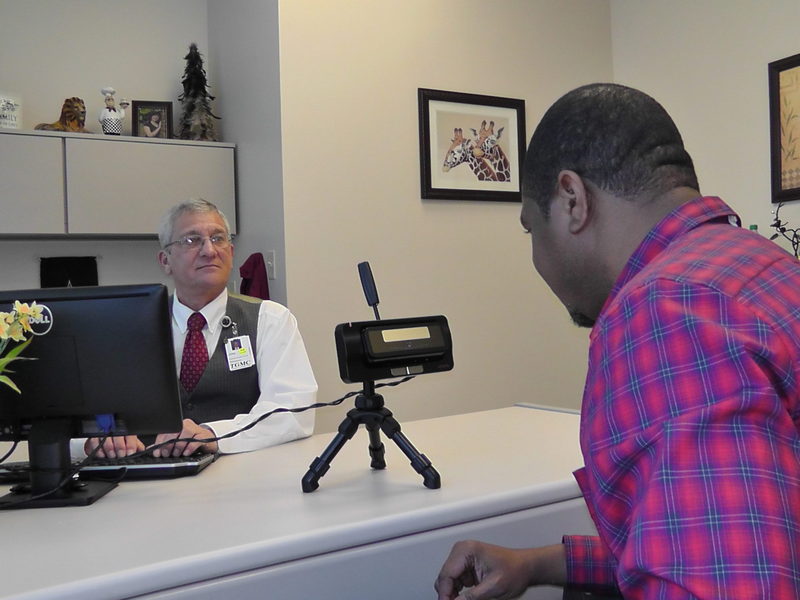
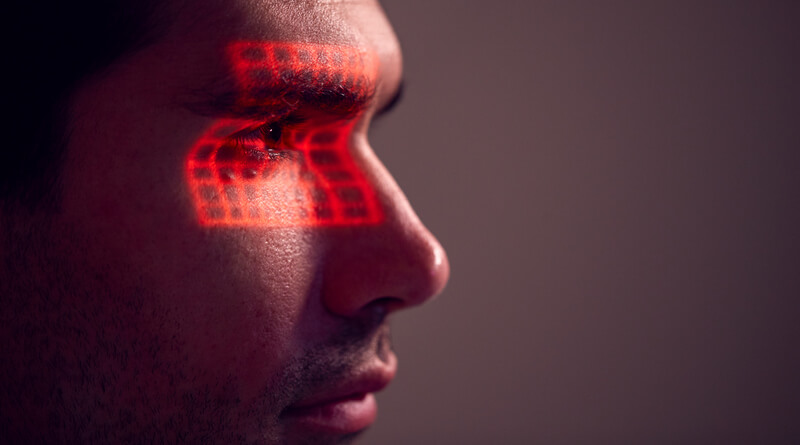
We have spent a lot of time during the past few years discussing how establishing accurate patient identification in healthcare with biometrics is the most effective technology to prevent:
— Duplicate medical records
— Healthcare fraud
— Medical identity theft
and improve:
— Patient safety
— Revenue cycle management

The use of biometrics for patient identification in healthcare helps HIM departments spend time on more value added services.
What often goes unnoticed is the impact that biometric patient identification solutions have on Health Information Management (HIM) departments. HIM departments carry tremendous responsibility on their shoulders in any healthcare organization acting as the entity in charge of providing and processing medical records containing patient information from pre-admission through discharge and afterward until the record is complete. This process includes:
— Preparing, indexing, and imaging all paper medical records
— Analyzing the health record for accuracy and to ensure it is completed
— Releasing patient information and protections assigned for closed-adoption, drug treatment, alcohol treatment, sexual, and behavioral health issues
— Coding for research, reimbursement, and provider report cards – coding personnel are responsible for abstracting diagnoses and procedures from medical records and assigning them a numerical code to ensure accurate billing and for data collection
— Analyzing active medical records to ensure all diagnoses are accurately documented
— Upon a client’s discharge from the hospital, process documents to provide relevant client demographic and medical information to the designated aftercare agencies to facilitate follow-up and continuity of the client’s care
Often considered the “medical record gatekeepers” of the healthcare industry, HIM departments perform one of the most critical functions in the healthcare work flow by ensuring the safety of patients through medical record accuracy. HIM also helps to facilitate fast and efficient payments under strict time constraints for services rendered, and spend a lot of time correcting patient records because healthcare facilities want to be paid on the care provided to patients in a timely fashion.
A large part of medical record reconciliation is resolving duplicate medical records and overlays (when two patients medical histories appear on one medical record) which consumes Full Time Equivalents (FTE’s), and swallows up resources that could otherwise be spent on more value-added tasks that directly impact revenue cycle management and limits penalties.
Litigation is also an important point to stress. A patient’s chart must be able to withstand the scrutiny of a legal proceeding if a patient were to sue a healthcare facility lending even more importance to the work of HIM to ensure medical record accuracy. There is also the issue of reporting. The HIM department is directly responsible that medical records are accurate for quality reporting which has a direct impact on reimbursement and avoiding penalties imposed by the Center for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) that range from readmissions to demonstrated improvement in patient outcomes. Keep in mind the new healthcare paradigm – stressing the quality vs. the quantity of services provided, a huge shift change that carries additional responsibility and an increased sense of urgency to ensure data accuracy at any healthcare facility.
Which brings us to the use of biometrics for accurate patient identification on the front end.
Healthcare facilities that have invested in deploying biometrics for accurate patient identification to prevent duplicate medical records and overlays on the front end are seeing the trickle down benefits to HIM departments, specifically the fact that they are spending less time reconciling duplicates and overlays and more time on coding, revenue cycle management, and reporting. It should be noted however, that biometric patient identification solutions built with search capabilities based on “one-to-many” matching types are the only solutions available that can truly prevent duplicate medical records, fraud, and medical identity at the point of registration. Do your homework before selecting a vendor, not all offer this type of back end matching capability.
Why is it important to reduce HIM FTEs spent on reconciliation of duplicate medical records and overlays? As noted earlier, many hospitals have expanded responsibilities vis-à-vis Meaningful Use, EHR implementation, and meeting Affordable Care Act requirements, and it has become disadvantageous to continue devoting any time at all to duplicate medical record and overlay reconciliation. Biometric patient identification solutions open the door to re-allocation of HIM FTEs to more critical functions such as coding, reimbursement, and reporting. Simply put, implementing biometrics during patient registration is opening the door for HIM departments across the industry to provide a larger and more productive support role to meet the shifting sands of reimbursement and address the need to move towards quality vs. quantity of care.
Hospitals should be actively seeking to deploy patient matching and patient identification technologies that eliminate barriers (e.g. duplicate medical records, overlays) and maximize HIM productivity to shift FTEs away from continuous master patient index (MPI) cleanup and more towards coding, quality review, reimbursement, and other areas. Many hospitals are already re-aligning their HIM departments in the wake of EHR implementation, and we expect to see more of the same for those using biometrics for accurate patient identification.
What other ways can the use of biometrics for patient identification reduce HIM FTEs?